- ENG
- KOR
WHY WAVE ENERGY?
The long-awaited blue energy with unlimited potential
Our planet’s perpetual waves have an energy potential of 3 TW, which is more energy than the world’s annual demand.
On top of that, the stronger waves that are used as energy sources can be found along every single continent and ocean around the world, proving that wave power generation has no territorial boundaries.
Distribution of the world wave energy potential
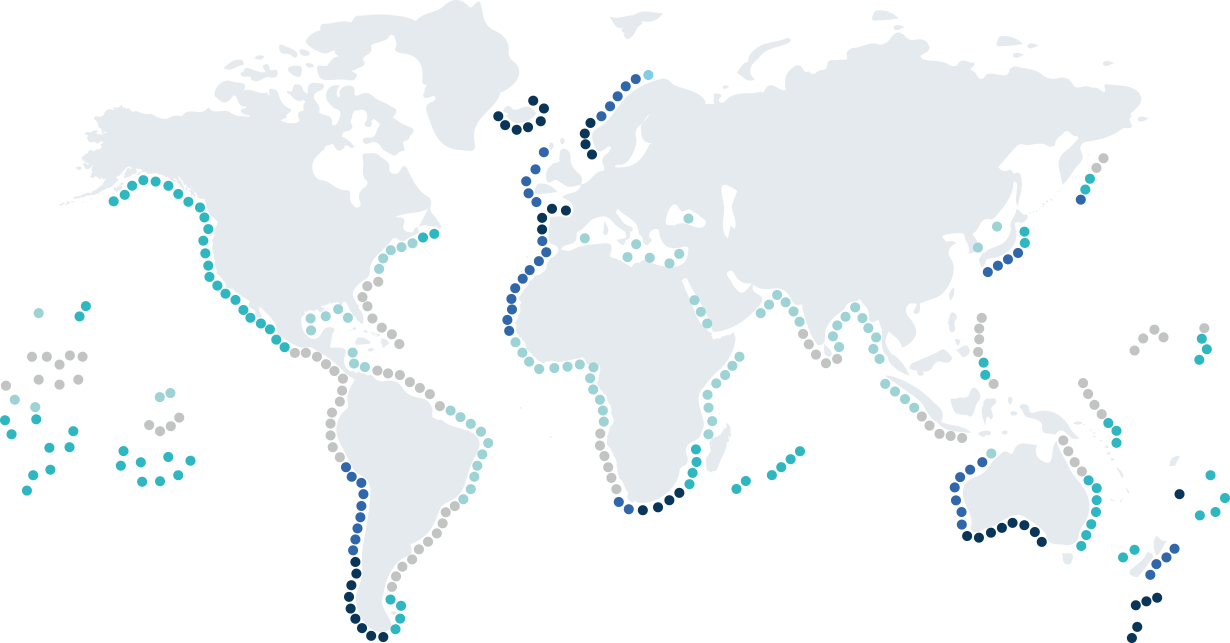
-
Europe
Many European coastal areas have strong waves, and each country is implementing progressive renewable energy policies.
Many leading marine energy companies
aim to realize RE100 initiatives on the European continent.
-
Asia
Despite being a neighboring country, Japan has much greater wave energy than Korea, making it a market with great potential. In the Asian region, there are many isolated islands that urgently need electricity, such as the islands of Indonesia and Vietnam, showing a strong need for wave power generation.
-
Oceania
This continent has great wave energy;
R&D on wave power is mainly being carried out in Australia.
-
Africa
Although geographically far from Korea,
the African continent has strong waves in the northeast and south, making it a suitable area for wave power generation.
-
North, Central, and
South AmericaIt is a large market where the energy demand is concentrated on the coastline, and wave energy is very strong from north to south.
- Unit (kW/m)
- 60~5050~4040~3030~2020~10
The clean energy with low carbon emissions
Waves are the source of marine energy that has the lowest carbon emissions,
even compared toother renewable energies like solar and wind power.
Additionally, this resource has great potential as it is the most abundant and widely distributed marine energy on Earth.
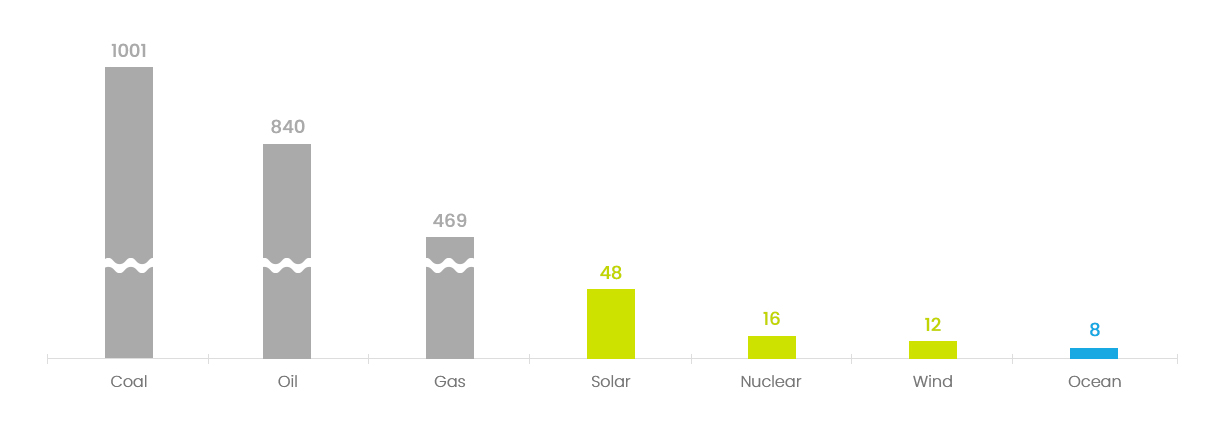
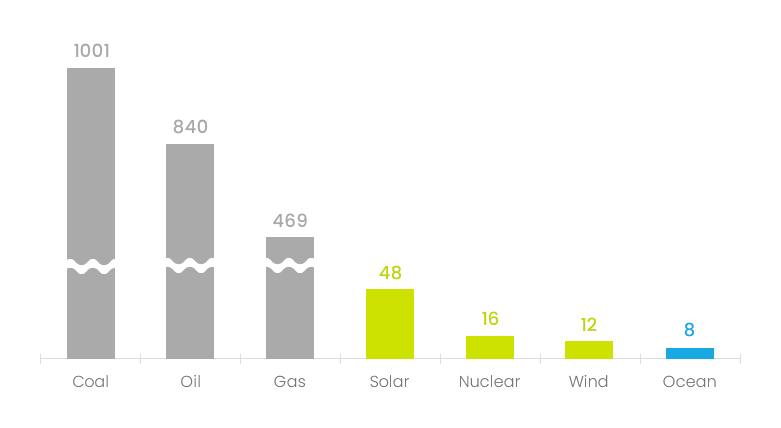
Lowest CO2 Emission
Unit : gCO2eg/kWh
Source : IPPC special Report on Renewable Energy Source and Climate Change Mitigation
The Safer Option with High Energy Density
Waves have a much higher energy density than wind or solar power, making them an cost-effective source of energy.
In addition, waves are considered to be a great energy source that is less volatile and more predictable than solar and wind power.
-

Average Solar Energy density
170~200W/m²
* Global solar electric potential
: A review of their technical and
sustainable limits -

Average Wind Density
200~800W/m²
* Ocean Wind Power Maps Reveal Possible
Wind Energy Sources -

Average Wave Energy Density
5,000~55,000W/m²
* Global Energy Network Institute





